Which Electrons From the Metal Make Up the Delocalized Electrons
This gives metals their malleability and luster. Each carbon atom has a delocalized electron that participates in chemical bonding but is free to move throughout the plane of the molecule.

Metallic Bonds Section 8 4 Sea Of Electrons Metal Atoms Contribute Their Valence E Delocalized Electrons E Are Free To Move Throughout The Solid B C Ppt Download
Delocalized electrons are electrons which are distributed and shared amongst more than two atoms through resonance.

. This problem has been solved. The delocalized electrons in the benzene ring make the molecule very stable and with its characteristics of a nucleophile it will react with a strong electrophile only and after the first reactivity the substituted benzene will depend on its resonance to direct the next position for the reaction to add a second substituent. That is instead of orbiting their respective metal atoms the electrons form a sea that surrounds the positively charged atomic nuclei of the interacting metal ions.
Metals form a giant structure like ionic compounds and giant molecules. Therefore these are delocalized electrons. The geometric shape model C.
The red electrons on the oxygen can participate in resonance stabilization because of the possibility of moving up the π bond electrons. Rules for drawing resonance contributors - only electrons move atoms never move - only π electrons and lone-pair electrons can move - the total number of electrons in the molecule does not change. 25 molar hydrochloric acid solution would be needed to react completely with 60.
The lithium atoms give up their outer electron in the valence shell to form lithium plus ions. The unit cell model B. While the electrons are delocalized graphite is a planar shape so the molecule conducts electricity along the plane but not perpendicular to it.
Electrons are not transfered completely like in ionic bonds. What explains the structure of metals and delocalized electrons. 9 What explains the structure of metals and delocalized electrons.
Are the metal atoms that are shown cations or anions. The structure of metallic bonds is very different from that of covalent and ionic bonds. 6 Which electrons from the metal make up the delocalized electrons.
Cations How do the metallic ions differ from the ions that exist in ionic solids. Delocalized electrons are contained within an orbital that extends over several adjacent atoms. 0 grams of calcium metal.
This free movement of delocalized electrons makes this type of bond unique as compared to ionic and covalent bonds where electrons must. The blue electrons on the other hand are localized on the top oxygen because the only way of moving them down would be either exceeding the octet of the carbon this really means there is no. Which electrons from the metal make up the delocalized electrons.
Definition for metallic bonds. Resonance is important when determining molecule reactivity and stability. The electron sea model 1 See answer Advertisement.
Delocalised means that the electrons are not attached to one particular ion. The covalent bond model D. Chemistry questions and answers.
Militers of a 1. Valence electrons in a metallic bond are delocalized and can move freely within the metal atoms. Metallic bonding may be described as the sharing of free electrons among a lattice of positively charged metal ions.
Delocalized electrons result from a p orbital overlapping the p orbital of two adjacent atoms. The valence electrons of the interacting metal atoms s and p orbitals delocalize in metallic bonds. 10 Which characteristics of metal atoms help explain why valence electrons in a metal are delocalized.
Delocalized electrons are electrons which are distributed and shared amongst more than two atoms through resonance. While the valence electron of each ion becomes delocalized and can hop freely from one ion to the next forming part of the sea of delocalized electrons. Lithium metal is a lattice of lithium.
Metals make up more than three-quarters of the elements. 11 Do metals easily give up. Resonance is important when determining molecule reactivity and stability.
The delocalised electrons between the positive metal ions. In the picture below the red balls represent metal ions. The blue lines represent delocalised electrons in the outer shell of the metal ions.
While ionic bonds join metals to nonmetals and covalent bonds join nonmetals to nonmetals metallic bonds are responsible for the bonding. One answer is that the outermost electrons only are very weakly bound and can be liberated with a small amount of energy and the heat available in a room temperature or even a very cold metal is very likely enough to destabilize this supposedly metastable state to decay into the lower energy delocalized state. Delocalized electrons are electrons in a molecule ion or solid metal that are not associated with a single atom or one covalent bond.

Metallic Bonding And The Electron Sea Model Electrical Conductivity Basic Introduction Youtube

Question Video Identifying The Number Of Electrons Contributed Per Metal Atom To The Sea Of Delocalized Electrons Nagwa
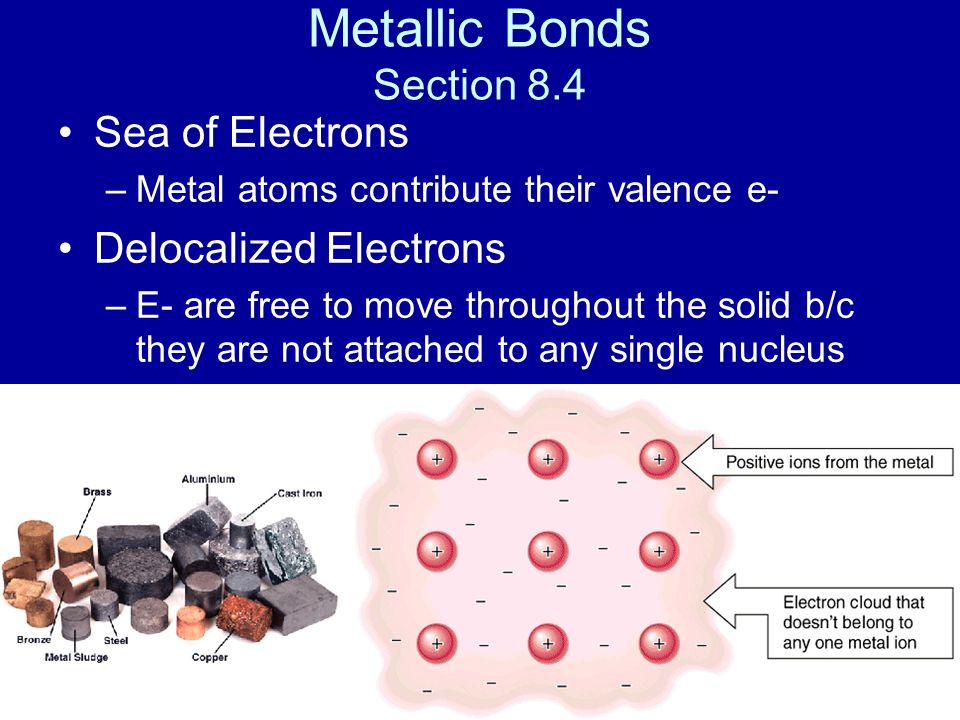
Metallic Bonds Section 8 4 Sea Of Electrons Metal Atoms Contribute Their Valence E Delocalized Electrons E Are Free To Move Throughout The Solid B C Ppt Download

Chemistry Metallic Bonds Sea Of Electrons Metal Atoms Contribute Their Valence Electrons Delocalized Electrons Electrons Are Free To Move Throughout Ppt Download
No comments for "Which Electrons From the Metal Make Up the Delocalized Electrons"
Post a Comment